Supabase SolidJS User Management
Usage
$ npm install
Learn more on the Solid Website and come chat with us on our Discord
Available Scripts
In the project directory, you can run:
npm dev or npm start
Runs the app in the development mode.
Open http://localhost:3000 to view it in the browser.
The page will reload if you make edits.
npm run build
Builds the app for production to the dist folder.
It correctly bundles Solid in production mode and optimizes the build for the best performance.
The build is minified and the filenames include the hashes.
Your app is ready to be deployed!
Build from scratch
1. Create new project
Sign up to Supabase - https://supabase.com/dashboard and create a new project. Wait for your database to start.
2. Run "User Management" Quickstart
Once your database has started, head over to your project's SQL Editor and run the "User Management Starter" quickstart. On the SQL editor page, scroll down until you see User Management Starter: Sets up a public Profiles table which you can access with your API. Click that, then click RUN to execute that query and create a new profiles table. When that's finished, head over to the Table Editor and see your new profiles table.
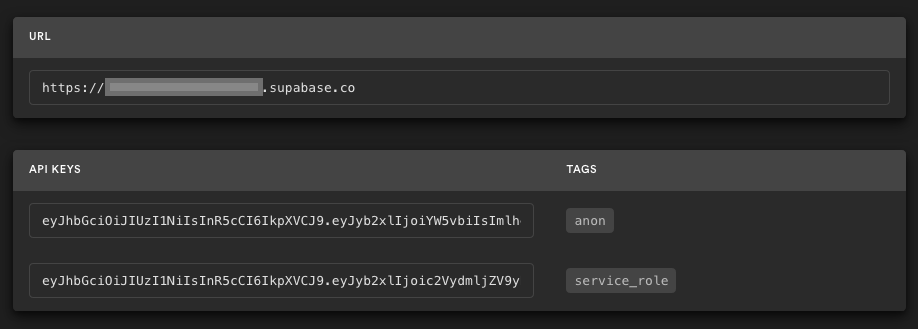
3. Get the URL and Key
Go to the Project Settings (the cog icon), open the API tab, and find your API URL and anon key, you'll need these in the next step.
The anon key is your client-side API key. It allows "anonymous access" to your database, until the user has logged in. Once they have logged in, the keys will switch to the user's own login token. This enables row level security for your data. Read more about this below.
NOTE: The service_role key has full access to your data, bypassing any security policies. These keys have to be kept secret and are meant to be used in server environments and never on a client or browser.
4. Env vars
Create .env.local from the .env.example file and populate this file with your URL and Key.
5. Run the application
Run the application: npm run dev. Open your browser to https://localhost:3000/ and you are ready to go 🚀.
Supabase details
Postgres Row level security
This project uses very high-level Authorization using Postgres' Row Level Security.
When you start a Postgres database on Supabase, we populate it with an auth schema, and some helper functions.
When a user logs in, they are issued a JWT with the role authenticated and their UUID.
We can use these details to provide fine-grained control over what each user can and cannot do.
This is a trimmed-down schema, with the policies:
-- Create a table for Public Profiles
create table
profiles (
id uuid references auth.users not null,
updated_at timestamp
with
time zone,
username text unique,
avatar_url text,
website text,
primary key (id),
unique (username),
constraint username_length check (char_length(username) >= 3)
);
alter table
profiles enable row level security;
create policy "Public profiles are viewable by everyone." on profiles for
select
using (true);
create policy "Users can insert their own profile." on profiles for insert
with
check ((select auth.uid()) = id);
create policy "Users can update own profile." on profiles for
update
using ((select auth.uid()) = id);
-- Set up Realtime!
begin;
drop
publication if exists supabase_realtime;
create publication supabase_realtime;
commit;
alter
publication supabase_realtime add table profiles;
-- Set up Storage!
insert into
storage.buckets (id, name)
values
('avatars', 'avatars');
create policy "Avatar images are publicly accessible." on storage.objects for
select
using (bucket_id = 'avatars');
create policy "Anyone can upload an avatar." on storage.objects for insert
with
check (bucket_id = 'avatars');
Authors
Supabase is open source. We'd love for you to follow along and get involved at https://github.com/supabase/supabase